Where's the Value?
From 1928–2017 the value premium1 in the U.S. had a positive annualized return of approximately 3.5%.2 In seven of the last 10 calendar years, however, the value premium in the U.S. has been negative.
This has prompted some investors to wonder if such an extended period of underperformance may be cause for concern. But are periods of underperformance in the value premium that unusual? We can look to history to help make sense of this question.
Short-Term Results
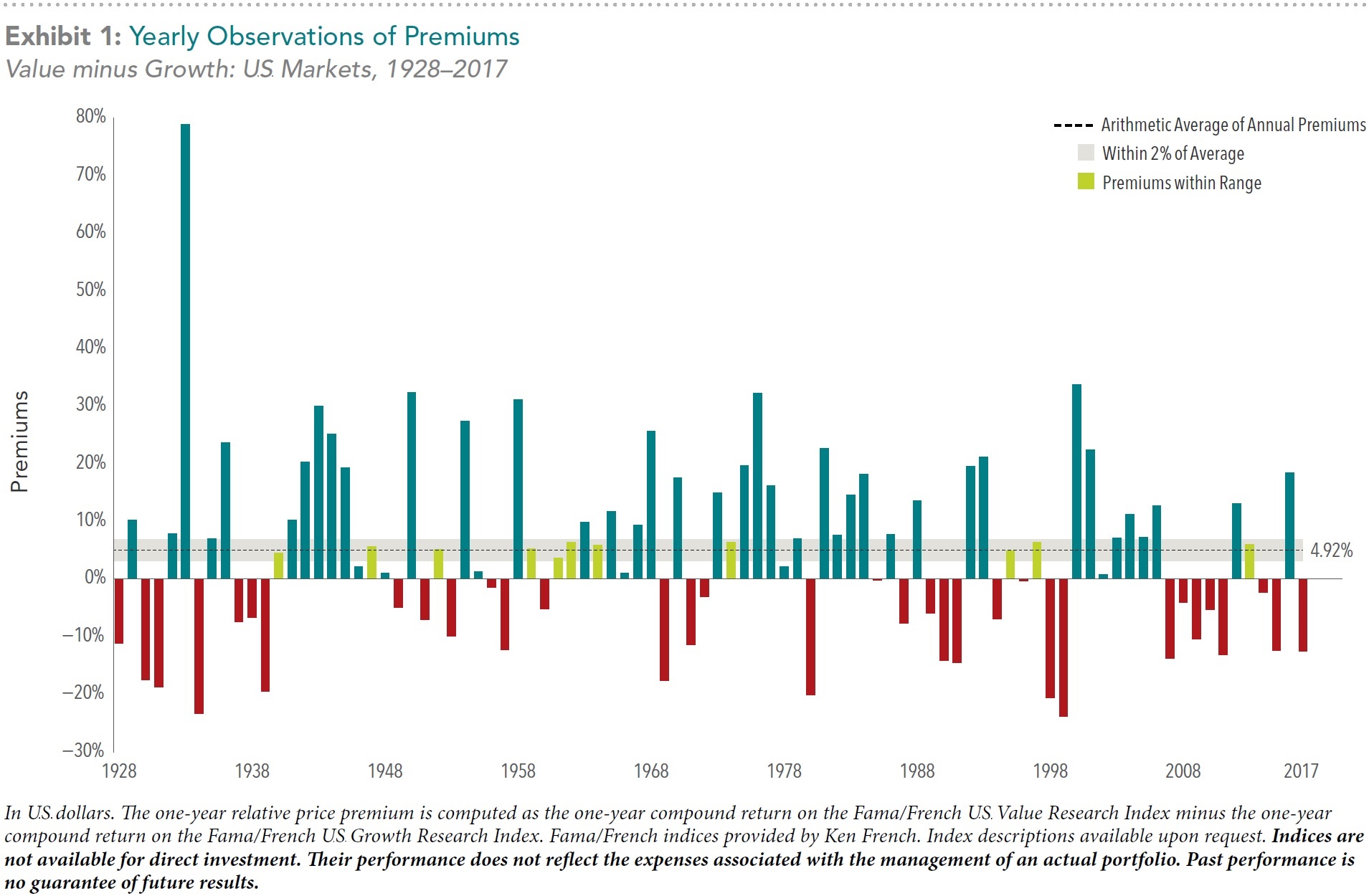
Exhibit 1 shows yearly observations of the U.S. value premium going back to 1928. We can see the annual arithmetic average for the premium is close to 5%, but in any given year the premium has varied widely, sometimes experiencing extreme positive or negative performance. In fact, there are only a handful of years that were within a 2% range of the annual average—most other years were farther above or below the mean. In the last 10 years alone there have been premium observations that were negative, positive, and in line with the historical average. This data helps illustrate that there is a significant amount of variability around how long it may take a positive value premium to materialize.
Long-Term Results
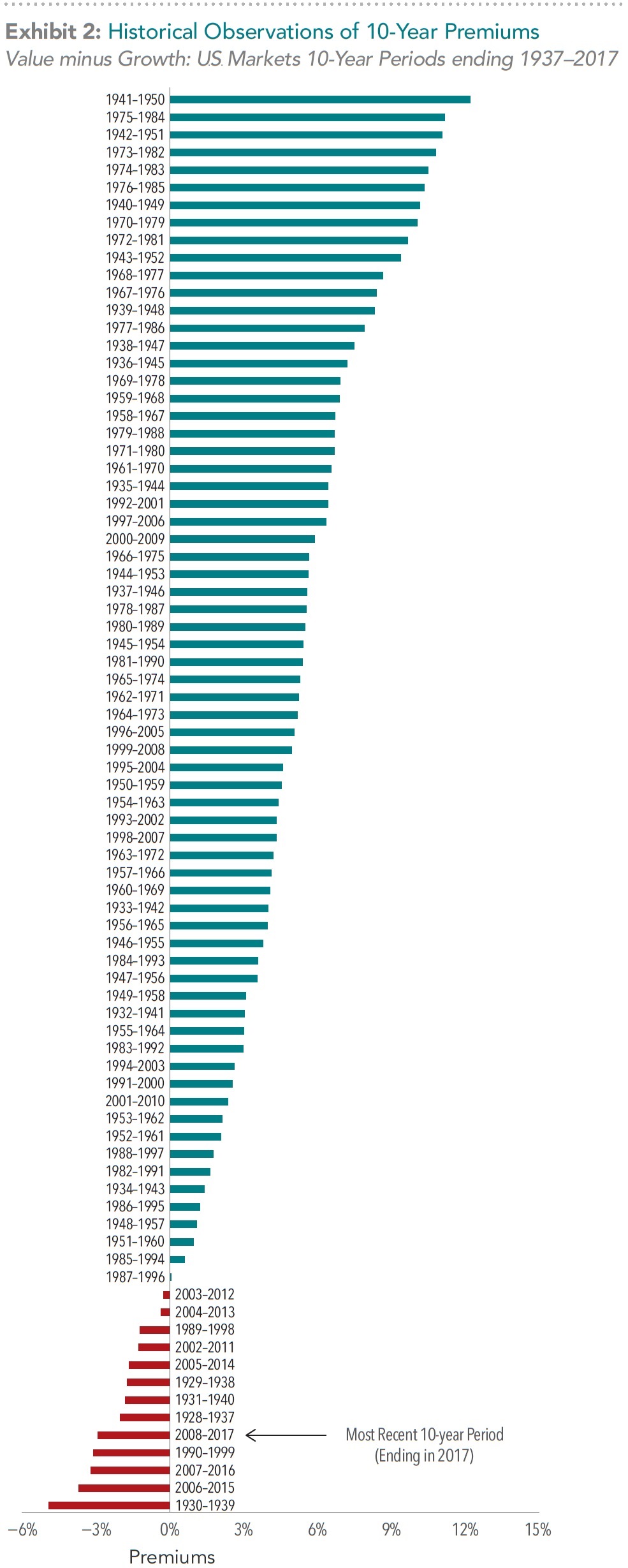
But what about longer-term underperformance? While the current stretch of extended underperformance for the value premium may be disappointing, it is not unprecedented. Exhibit 2 documents 10-year annualized performance periods for the value premium, sorted from lowest to highest by end date (calendar year). The earliest 10-year period in the series began in 1928 and ended in 1937.
This chart shows us that the best 10-year period for the value premium was from 1941–1950 (at the top), while the worst was from 1930–1939 (at the bottom). In most cases, we can see that the value premium was positive over a given 10-year period. As the arrow indicates, however, the value premium for the most recent 10-year period (ending in 2017) was negative. To put this in context, the most recent 10 years is one of only 13 periods since 1937 that had a negative annualized value premium. Of these, the most recent period of underperformance has been fairly middle-of-the-road in magnitude.

Frequency of Long-Term Results
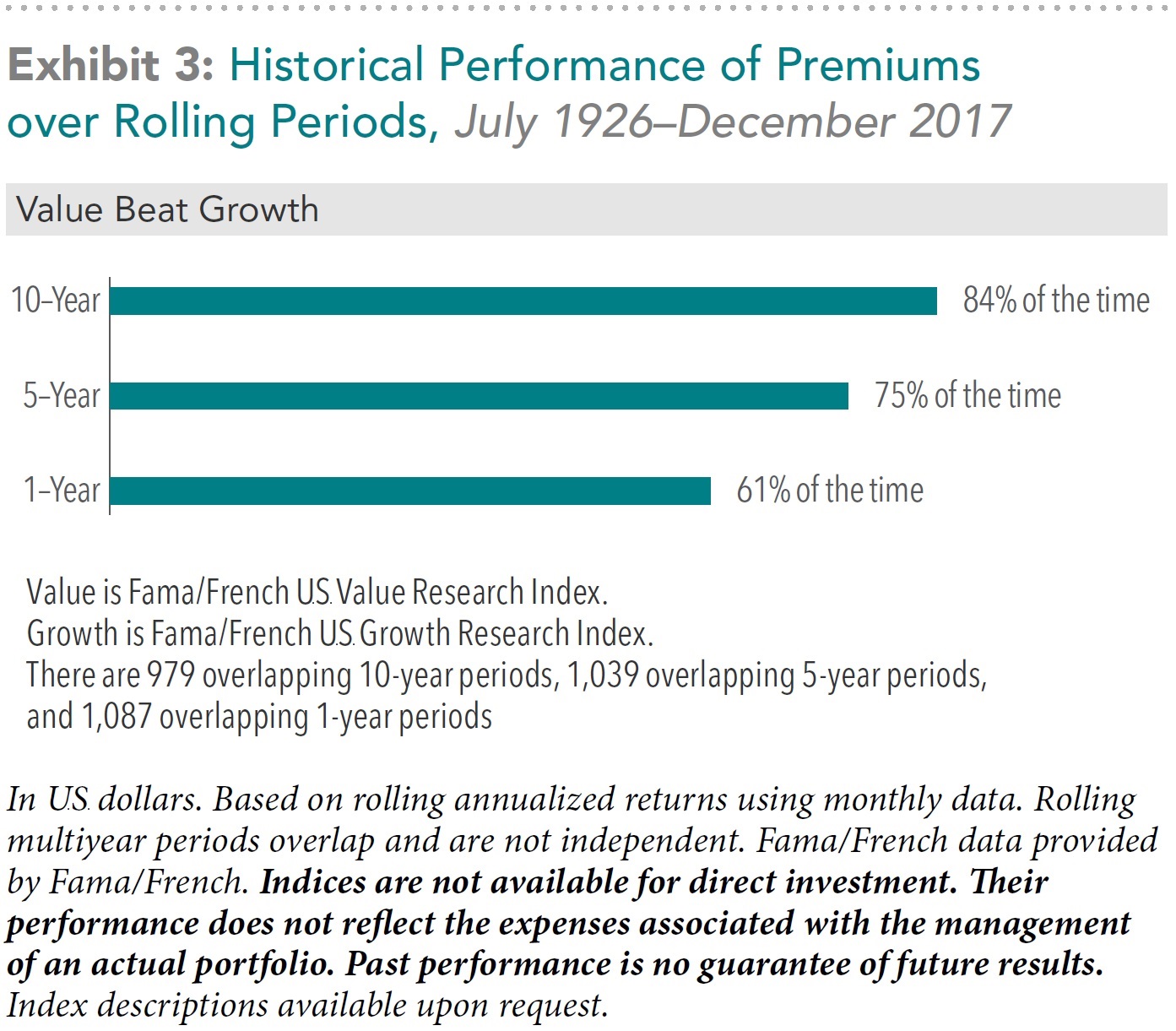
While there is uncertainty around how long periods of underperformance may last, historically the frequency of a positive value premium has increased over longer time horizons. Exhibit 3 shows the percentage of time that the value premium was positive over different time periods going back to 1926. When the length of time measured increased, the chance of a positive value premium increased. For example, when the time period measured goes from five years to 10 years, the frequency of positive average premiums increased from 75% to 84%.
Maintaining Consistency
What does all this mean for investors? While a positive value premium is never guaranteed, the premium has historically had a greater chance of being positive the longer the time horizon observed. Even with long-term positive results though, periods of extended underperformance can happen from time to time. Because the value premium has not historically materialized in a steady or predictable fashion, a consistent investment approach that maintains an emphasis on value stocks in all market environments may allow investors to more reliably capture the premium over the long run. Additionally, keeping implementation costs low and integrating multiple dimensions of expected stock returns (such as size and profitability) can improve the consistency of expected outperformance.
[1] The value premium is the return difference between stocks with low relative prices (value) and stocks with high relative prices (growth).
[2] Computed as the return difference between the Fama/French U.S. Value Research Index and the Fama/French U.S. Growth Research Index. Fama/French indices provided by Ken French.
Past performance does not guarantee future results. All investments include risk and have the potential for loss as well as gain.
Data sources for returns and standard statistical data are provided by the sources referenced and are based on data obtained from recognized statistical services or other sources we believe to be reliable. However, some or all information has not been verified prior to the analysis, and we do not make any representations as to its accuracy or completeness. Any analysis nonfactual in nature constitutes only current opinions, which are subject to change. Benchmarks or indices are included for information purposes only to reflect the current market environment; no index is a directly tradable investment. There may be instances when consultant opinions regarding any fundamental or quantitative analysis do not agree.
The commentary contained herein has been compiled by W. Reid Culp, III from sources provided by TAGStone Capital, Capital Directions, DFA, Vanguard, Morningstar, as well as commentary provided by Mr. Culp, personally, and information independently obtained by Mr. Culp. The pronoun “we,” as used herein, references collectively the sources noted above.
TAGStone Capital, Inc. provides this update to convey general information about market conditions and not for the purpose of providing investment advice. Investment in any of the companies or sectors mentioned herein may not be appropriate for you. You should consult your advisor from TAGStone for investment advice regarding your own situation.
